
Show UniFi server logs with: cat /mnt/data/unifi-os/unifi/logs/server.log You can use view the specific logs you’re interested in by using the cat command, or view live logs with tail.
#Putty ssh username how to#
This is Ubiquiti's help article for how to retrieve log files. Refer to the commands on the right side of the table Retrieve Log Files This reddit thread shows a good list of these unique commands, file locations, and what they are good for. There are also some commands and files that are unique to the UDM and not well documented by Ubiquiti. Standard Linux commands like ifconfig, tcpdump, netstat, whoami and cat are also available.
Typing “help” shows an incomplete list of the commands that are available:īuilt-in commands available to root user: With that said, there’s still a few things you can do.
#Putty ssh username install#
You are not allowed to install packages or modify things like you might be used to on other Linux-based devices. UbiOS/UniFi OS is based on Buildroot Linux, and is Ubiquiti’s custom implementation.
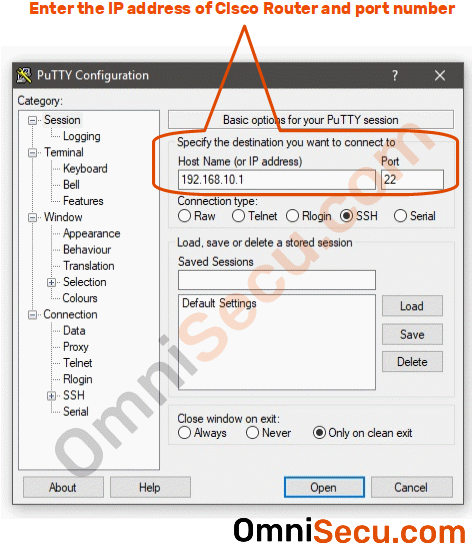
The Unifi service or a firmware update will overwrite most things you can change. The UDM doesn’t have a configuration shell, you will only have direct Linux shell access. With the UDM, you have to make your permanent configuration changes through the web UI. The “configuration” part doesn’t really apply to the UDM, though. The one sentence summary is that SSH allows for a safe way to read and write the configuration, access logs, and troubleshoot problems. If you’re not familar with SSH, Ubiquiti has a good help page which introduces what SSH is and how it works. If this is your first time accessing the device, accept the authenticity of the host key by typing yes and hit enterĪccess the UniFi OS shell by typing unifi-os shell and hit enter Replace the IP, but the username is always root. If your IP address is 192.168.1.1, you’d type ssh and hit enter. Windows = PuTTY, or enable the new built-in Windows Terminal in Windows 10. There are many applications that you can use, but some quick recommendations based on your OS: Open your terminal application of choice. SSH into the UDM with the username of “root” and the password you just set


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
